Another form of CSMA used by IEEE 802.11 WLANs is carrier sense multiple access/collision avoidance (CSMA/CA).
CMSA/CA uses a method similar to CSMA/CD to detect if the media is clear. CMSA/CA uses additional techniques. In wireless environments it may not be possible for a device to detect a collision. CMSA/CA does not detect collisions but attempts to avoid them by waiting before transmitting. Each device that transmits includes the time duration that it needs for the transmission. All other wireless devices receive this information and know how long the medium will be unavailable.
In Figure 31-16, if host A is receiving a wireless frame from the access point, hosts B, and C will also see the frame and how long the medium will be unavailable.
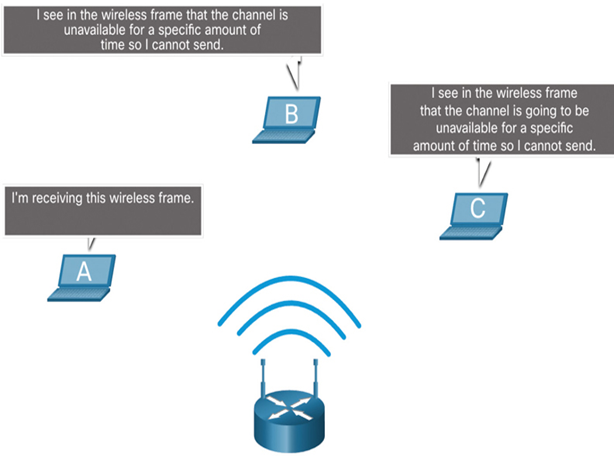
Figure 31-16 CSMA/CA
After a wireless device sends an 802.11 frame, the receiver returns an acknowledgment so that the sender knows the frame arrived.
Whether it is an Ethernet LAN using hubs, or a WLAN, contention-based systems do not scale well under heavy media use.
Note:
Ethernet LANs using switches do not use a contention-based system because the switch and the host NIC operate in full-duplex mode.
Check Your Understanding – Media Access Control Methods (31.2.5)
Refer to the online course to complete this Activity.
The following is a summary of each topic in the chapter and some questions for your reflection.
What Did I Learn in this Module? (31.3.1)
• Topologies—The two types of topologies used in LAN and WAN networks are physical and logical. The data link layer “sees” the logical topology of a network when controlling data access to the media. The logical topology influences the type of network framing and media access control used. Three common types of physical WAN topologies are: point-to-point, hub and spoke, and mesh. Physical point-to-point topologies directly connect two end devices (nodes). Adding intermediate physical connections may not change the logical topology. In multiaccess LANs, nodes are interconnected using star or extended star topologies. In this type of topology, nodes are connected to a central intermediary device.
Physical LAN topologies include: star, extended star, bus, and ring. Half-duplex communications exchange data in one direction at a time. Full-duplex sends and receives data simultaneously. Two interconnected interfaces must use the same duplex mode or there will be a duplex mismatch creating inefficiency and latency on the link. Ethernet LANs and WLANs are examples of multiaccess networks. A multiaccess network is a network that can have multiple nodes accessing the network simultaneously.
• Media Access Control Methods—Some multiaccess networks require rules to govern how devices share the physical media. There are two basic access control methods for shared media: contention-based access and controlled access. In contention-based multiaccess networks, all nodes are operating in half-duplex. There is a process if more than one device transmits at the same time. Examples of contention-based access methods include: CSMA/CD for bus-topology Ethernet LANs and CSMA/CA for WLANs.
Halimah had to examine the network at her headquarters in Nigeria. She is very experienced with creating topologies. The two types of topologies used in LAN and WAN networks are physical and logical. Halima can easily create and interpret topologies.
Can you draw a topology of your home network? That may be a bit simpler than the topology in your office building.
What type of topology do you think your office building has? Consider asking someone in your IT department if you can look at the topology.
