This section introduces the two types of IPv6 multicast addresses: well-known multicast and solicited-node multicast addresses.
Assigned IPv6 Multicast Addresses (33.5.1)
Earlier in this chapter, you learned that there are three broad categories of IPv6 addresses: unicast, anycast, and multicast. This section goes into more detail about multicast addresses.
IPv6 multicast addresses are similar to IPv4 multicast addresses. Recall that a multicast address is used to send a single packet to one or more destinations (multicast group). IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix ff00::/8.
Note
Multicast addresses can only be destination addresses and not source addresses.
There are two types of IPv6 multicast addresses:
• Well-known multicast addresses
• Solicited-node multicast addresses
Well-Known IPv6 Multicast Addresses (33.5.2)
Well-known IPv6 multicast addresses are assigned. Assigned multicast addresses are reserved multicast addresses for predefined groups of devices. An assigned multicast address is a single address used to reach a group of devices running a common protocol or service. Assigned multicast addresses are used in context with specific protocols such as DHCPv6.
These are two common IPv6 assigned multicast groups:
• ff02::1 All-nodes multicast group—This is a multicast group that all IPv6-enabled devices join. A packet sent to this group is received and processed by all IPv6 interfaces on the link or network. This has the same effect as a broadcast address in IPv4. Figure 33-18 shows an example of communication using the all-nodes multicast address. An IPv6 router sends ICMPv6 RA messages to the all-nodes multicast group.
• ff02::2 All-routers multicast group—This is a multicast group that all IPv6 routers join. A router becomes a member of this group when it is enabled as an IPv6 router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command. A packet sent to this group is received and processed by all IPv6 routers on the link or network.
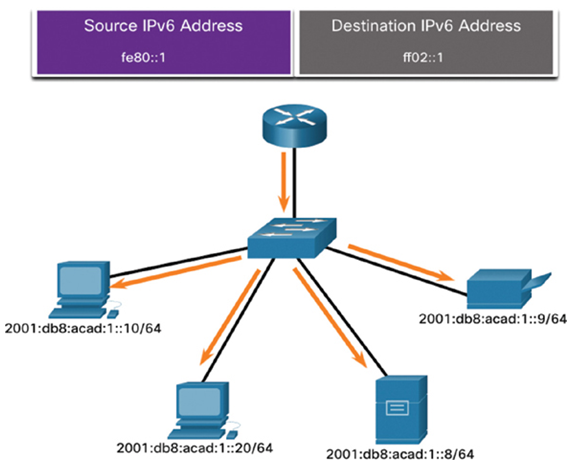
Figure 33-18 IPv6 All-Nodes Multicast: RA Message
The fourth digit in the address refers to the scope. A 2 for the scope indicates that these addresses have “link-local scope,” meaning packets with this destination address are not be routed off this link or network.
IPv6-enabled devices send ICMPv6 RS messages to the all-routers multicast address. The RS message requests an RA message from the IPv6 router to assist the device in its address configuration. The IPv6 router responds with an RA message, as shown in Figure 33-18.
Solicited-Node IPv6 Multicast Addresses (33.5.3)
A solicited-node multicast address is similar to the all-nodes multicast address. The advantage of a solicited-node multicast address is that it is mapped to a special Ethernet multicast address. This allows the Ethernet NIC to filter the frame by examining the destination MAC address without sending it to the IPv6 process to see if the device is the intended target of the IPv6 packet, as shown in Figure 33-19.
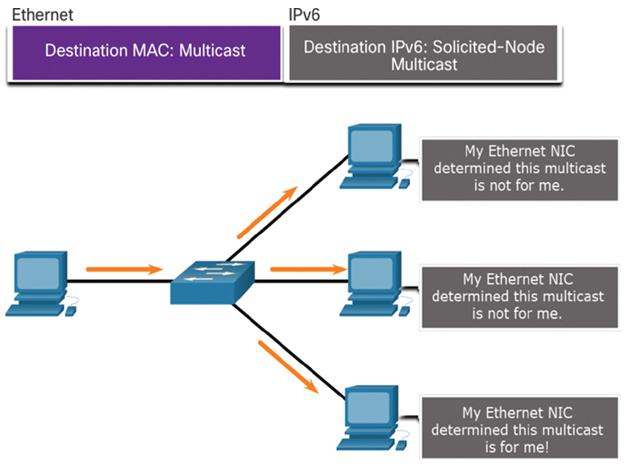
Figure 33-19 Solicited-Node IPv6 Multicast Example
