Coaxial was one of the earliest types of network cabling developed. Coaxial cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies. It is also used for connecting the various components which make up satellite communication systems. Coaxial cable has a single rigid copper core that conducts the signal, as shown in Figure 6-3. This core is typically surrounded by a layer of insulation, braided metal shielding, and a protective jacket. It is used as a high-frequency transmission line to carry high-frequency or broadband signals.

Figure 6-3 An Example of a Coaxial Cable
Fiber-optic Cable
Fiber-optic cable can be either glass or plastic with a diameter about the same as a human hair and it can carry digital information at very high speeds over long distances. Because light is used instead of electricity, electrical interference does not affect the signal. Fiber-optic cables, shown in Figure 6-4, have many uses as well as communications. They are also used in medical imaging, medical treatment, and mechanical engineering inspection.
They have a very high bandwidth, which enables them to carry very large amounts of data. Fiber is used in backbone networks, large enterprise environments, and large data centers. It is also used extensively by telephone companies.
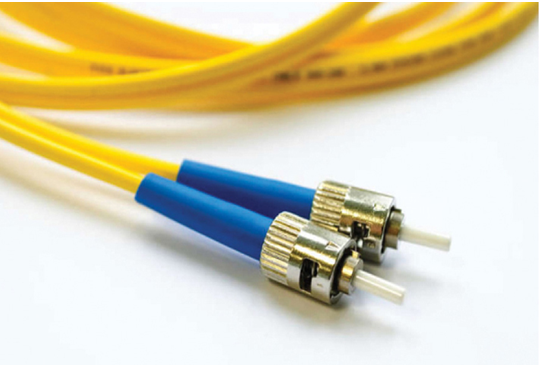
Figure 6-4 An Example of Fiber-Optic Cable
The following is a summary of each topic in the chapter and some questions for your reflection.
What Did I Learn in this Module? (6.2.1)
Communication transmits across a network on media. The media provides the channel over which the message travels from source to destination.
Modern networks primarily use three types of media to interconnect devices are:
• Metal wires within cables – Data is encoded into electrical impulses.
• Glass or plastic fibers within cables (fiber-optic cable) – Data is encoded into pulses of light.
• Wireless transmission – Data is encoded via modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves.
The four main criteria for choosing media are the following:
• What is the maximum distance that the media can successfully carry a signal?
• What is the environment in which the media will be installed?
• What is the amount of data and at what speed must it be transmitted?
• What is the cost of the media and installation?
The three most common network cables are twisted-pair, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable. Ethernet technology generally uses twisted-pair cables to interconnect devices. Coaxial cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies. It is also used for connecting the various components which make up satellite communication systems. Fiber-optic cable can be either glass or plastic with a diameter about the same as a human hair and it can carry digital information at very high speeds over long distances. Because light is used instead of electricity, electrical interference does not affect the signal.
I had no idea that a network needed to have different cables for different uses, did you? I thought all the cables were the same and that they all carried the same type of signal. And electrical interference? Now I get why my smartphone connection sometimes drops if I stand too close to my microwave! Do you know about all the cables that are used in your school or office network?
