Before entering the configuration utility, or manually configuring the router through a web browser, you should consider how your network will be used. You do not want to configure the router and have that configuration limit what you are able to do on the network, nor do you want to leave your network unprotected.
What should my network be called?
If SSID broadcasting is on, the SSID name will be seen by all wireless clients within your signal range. Many times the SSID gives away too much information about the network to unknown client devices. It is not a good practice to include the device model or brand name as part of the SSID. Wireless devices have default settings that are easy to find on the internet, as well as known security weaknesses.
What types of devices will attach to my network?
Wireless devices contain radio transmitter/receivers that function within a specific frequency range. If a device only has the necessary radio for 802.11 b/g, it will not connect if the wireless router or access point is configured to only accept 802.11n or 802.11ac standards. If all devices support the same standard, the network will work at its optimum speed. If you have devices that do not support the n or ac standards, then you will have to enable legacy mode. A legacy mode wireless network environment varies between router models but can include a combination of 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac. This environment provides easy access for legacy devices that need a wireless connection.
The decision regarding who can access your home network should be determined by how you plan to use the network. On some wireless routers, it is possible to set up guest access. This is a special SSID coverage area that allows open access but restricts that access to using the internet only.
The Figure 4-8 shows a wireless setup screen.
Note
Some wireless routers may label legacy mode as mixed mode.
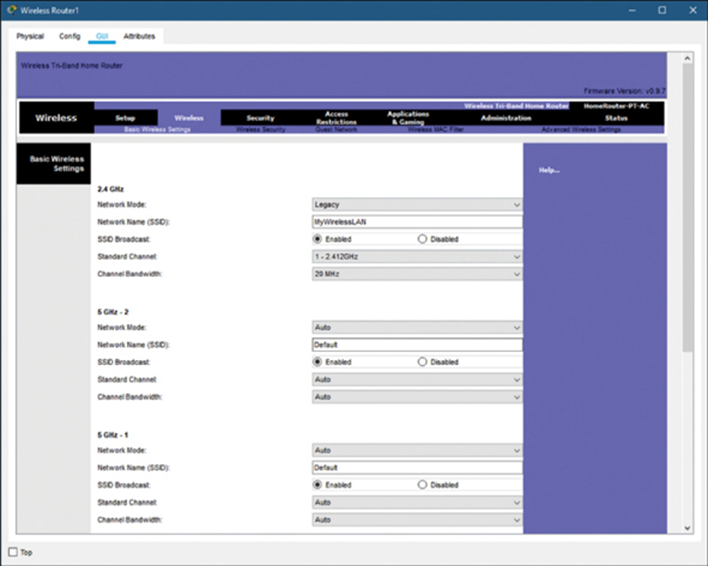
Figure 4-8 Packet Tracer WLAN Configuration Example
In this Packet Tracer activity, you will complete the following objectives.
• Part 1: Connect the Devices
• Part 2: Configure the Wireless Router
• Part 3: Configure IP Addressing and Test Connectivity
Refer to the online course to complete this activity.
