Dynamic Addressing for IPv6 GUAs (33.3)
This section discusses the different methods of how a device can automatically create or receive an IPv6 GUA.
RS and RA Messages (33.3.1)
If you do not want to statically configure IPv6 GUAs, no need to worry. Most devices obtain their IPv6 GUAs dynamically. This topic explains how this process works using Router Advertisement (RA) and Router Solicitation (RS) messages. This topic gets rather technical, but when you understand the difference between the three methods that a router advertisement can use, as well as how the EUI-64 process for creating an interface ID differs from a randomly generated process, you will have made a huge leap in your IPv6 expertise!
For the GUA, a device obtains the address dynamically through Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) messages. IPv6 routers periodically send out ICMPv6 RA messages, every 200 seconds, to all IPv6-enabled devices on the network. An RA message will also be sent in response to a host sending an ICMPv6 RS message, which is a request for an RA message. Both messages are shown in Figure 33-10.
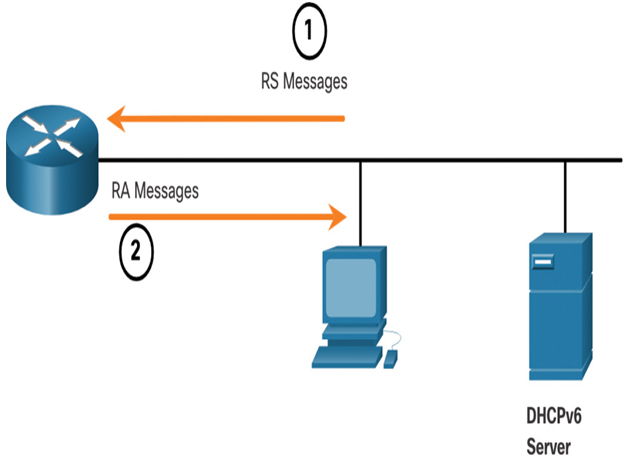
Figure 33-10 ICMPv6 RS and RA Messages
- RS messages are sent to all IPv6 routers by hosts requesting addressing information.
- RA messages are sent to all IPv6 nodes. If Method 1 (SLAAC only) is used, the RA includes network prefix, prefix length, and default gateway information.
RA messages are on IPv6 router Ethernet interfaces. The router must be enabled for IPv6 routing, which is not enabled by default. To enable a router as an IPv6 router, the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command must be used.
The ICMPv6 RA message is a suggestion to a device on how to obtain an IPv6 GUA. The ultimate decision is up to the device operating system. The ICMPv6 RA message includes the following:
- Network prefix and prefix length—This tells the device which network it belongs to.
- Default gateway address—This is an IPv6 LLA, the source IPv6 address of the RA message.
- DNS addresses and domain name—These are the addresses of DNS servers and a domain name.
There are three methods for RA messages: - Method 1: SLAAC—“I have everything you need including the prefix, prefix length, and default gateway address.”
- Method 2: SLAAC with a stateless DHCPv6 server—“Here is my information but you need to get other information such as DNS addresses from a stateless DHCPv6 server.”
- Method 3: Stateful DHCPv6 (no SLAAC)—“I can give you your default gateway address. You need to ask a stateful DHCPv6 server for all your other information.”
