Before configuring SSH, the switch must be minimally configured with a unique hostname and the correct network connectivity settings.
Step 1. Verify SSH support.
Use the show ip ssh command to verify that the switch supports SSH. If the switch is not running an IOS that supports cryptographic features, this command is unrecognized.
Step 2. Configure the IP domain.
Configure the IP domain name of the network using the ip domain-name domain-name global configuration mode command. In the example configuration below, the domain-name value is cisco.com.
Step 3. Generate RSA key pairs.
Not all versions of the IOS default to SSH version 2, and SSH version 1 has known security flaws. To configure SSH version 2, issue the ip ssh version 2 global configuration mode command. Generating an RSA key pair automatically enables SSH. Use the crypto key generate rsa global configuration mode command to enable the SSH server on the switch and generate an RSA key pair. When generating RSA keys, the administrator is prompted to enter a modulus length. The sample configuration in the figure uses a modulus size of 1,024 bits. A longer modulus length is more secure, but it takes more time to generate and to use.
Note:
To delete the RSA key pair, use the crypto key zeroize rsa global configuration mode command. After the RSA key pair is deleted, the SSH server is automatically disabled.
Step 4. Configure user authentication.
The SSH server can authenticate users locally or use an authentication server. To use the local authentication method, create a username and password pair with the username username secret password global configuration mode command. In the example, the user admin is assigned the password ccna.
Step 5. Configure the vty lines.
Enable the SSH protocol on the vty lines using the transport input ssh line configuration mode command. The Catalyst 2960 has vty lines ranging from 0 to 15. This configuration prevents non-SSH (such as Telnet) connections and limits the switch to accept only SSH connections. Use the line vty global configuration mode command and then the login local line configuration mode command to require local authentication for SSH connections from the local username database.
Step 6. Enable SSH version 2.
By default, SSH supports both versions 1 and 2. When supporting both versions, this is shown in the show ip ssh output as supporting version 1.99. Version 1 has known vulnerabilities. For this reason, it is recommended to enable only version 2. Enable SSH version using the ip ssh version 2 global configuration command.
Syntax Checker – Configure SSH (28.3.4)
Use this Syntax Checker to configure SSH on switch S1
Refer to the online course to complete this Activity.
On a PC, an SSH client such as PuTTY, is used to connect to an SSH server. For the examples, the following have been configured:
• SSH enabled on switch S1
• Interface VLAN 99 (SVI) with IPv4 address 172.17.99.11 on switch S1
• PC1 with IPv4 address 172.17.99.21
In Figure 28-1, the technician is initiating an SSH connection to the SVI VLAN IPv4 address of S1. The terminal software PuTTY is shown.
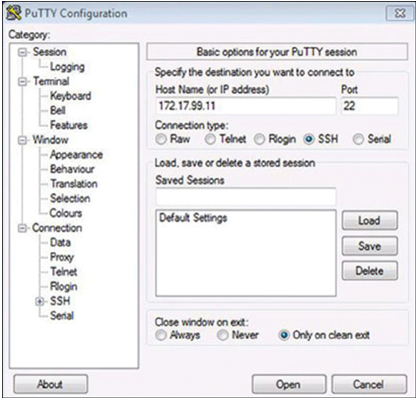
Figure 28-1 SSH connection with Putty
After clicking Open in PuTTY, the user is prompted for a username and password. Using the configuration from the previous example, the username admin and password ccna are entered. After entering the correct combination, the user is connected via SSH to the CLI on the Catalyst 2960 switch.
To display the version and configuration data for SSH on the device that you configured as an SSH server, use the show ip ssh command. In Example 28-9, SSH version 2 is enabled. To check the SSH connections to the device, use the show ssh command.
Packet Tracer – Configure SSH (28.3.6)
In this activity, you will complete the following objectives:
• Secure Passwords
• Encrypt Communications
• Verify SSH Implementation
Refer to the online course to complete this Activity.
